
Tax mitigation strategies are essential for maximizing investment returns and preserving wealth, particularly in real estate. For investors, exploring different approaches to reduce tax liability can significantly enhance overall portfolio performance. In this blog, we’ll examine three key tax mitigation strategies for real estate investors: Opportunity Zones, 1031 Exchanges, and Delaware Statutory Trusts (DSTs). By understanding the unique advantages and potential downsides of each, you can make informed decisions to optimize your financial planning and confidently navigate today’s evolving economic landscape.
What is a Qualified Opportunity Zone?
Opportunity Zones were created under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 as an innovative approach to spur economic growth and development in designated low-income communities across the United States. These zones are specific geographic areas, nominated by state governors and certified by the U.S. Treasury Department, that offer significant tax incentives for investors willing to commit their capital to long-term projects within these regions.
Deferred capital gains tax: By investing in a Qualified Opportunity Fund (QOF) – the vehicle used to invest in Opportunity Zone properties – you can defer your capital gains tax liability from the sale of a prior investment. Provided that the investment is made within 180 days of the recognition date. These gains can originate from various types of asset sales, including real estate, publicly traded securities (stocks, bonds, mutual funds, ETFs), privately held businesses, collectibles, or crypto assets like Bitcoin. Keep in mind that it is possible to invest more than the eligible gain, but only the capital gain portion would be eligible for the tax benefits.
The deferred capital gains tax must be paid by December 31, 2026, or when the Opportunity Zone investment is sold, whichever comes first.
Tax-free appreciation: If you maintain your investment in a QOF for at least ten years, you’ll benefit from tax-free appreciation on the Opportunity Zone investment. This means that any capital gains realized upon the sale of the investment after the ten-year holding period will be exempt from federal capital gains tax, as long as the gain from the Opportunity Zone investment is recognized by December 31, 2047.
While Opportunity Zones offer attractive tax benefits, investors should also be aware of potential drawbacks and risks. Some concerns include :
Long-term commitment: To reap the full benefits of Opportunity Zone investments, you’ll need to be prepared for a long-term commitment, as holding periods of at least ten years are required for tax-free appreciation.
Liquidity concerns: Due to the long-term nature of these investments, they may not be suitable for investors seeking short-term liquidity or those who may need access to their capital sooner.
Investment risk: As with any investment, there are risks associated with investing in Opportunity Zones. The potential for economic growth in Opportunity Zones varies greatly depending on factors such as local infrastructure, job market, and population trends. Some zones may not experience the desired level of growth, limiting the appreciation potential of your investment. Investing in low-income areas can also carry additional risks, such as higher crime rates, lower property values, and slower economic growth. It’s also important to understand that the Opportunity Zones program is a government-created incentive, changes in legislation, regulation, or government policy could affect the benefits and long-term viability of these investments. Other risks may include market fluctuations, project development risks
Opportunity Zones can offer significant tax advantages for investors willing to commit to long-term investments in designated low-income communities. However, it’s essential to weigh the potential drawbacks and assess whether this strategy aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Another tax-saving strategy for investors is the 1031 Exchange, which gets its name from Section 1031 of the Internal Revenue Code. The 1031 Exchange allows investors to defer capital gains taxes on the sale of an investment property by reinvesting the proceeds into a like-kind property. This strategy is particularly popular among real estate investors looking to optimize their portfolio while minimizing tax liability.
Deferral of capital gains tax: By participating in a 1031 Exchange, investors can defer capital gains taxes on the sale of an investment property, allowing them to reinvest the full sale proceeds into a new property and potentially achieve higher returns.
Portfolio diversification and growth: Investors can leverage 1031 Exchanges to diversify their real estate portfolio by acquiring properties with different characteristics, locations, or investment objectives. This strategy can help investors manage risk and enhance the overall performance of their portfolio.
Estate planning benefits: 1031 Exchanges can also be utilized as part of an investor’s estate planning strategy, allowing them to pass on a stepped-up basis market-rate value to their heirs. In this scenario, the heirs would only be liable for taxes on future gains rather than the deferred gains from previous exchanges.
While 1031 Exchanges offer significant tax benefits, they also come with specific rules and requirements that investors must adhere to, such as:
Strict timeframes: Investors have 45 days from the sale of their original property to identify a replacement property and 180 days to complete the purchase. Failure to meet these deadlines may result in the disqualification of the exchange and the realization of capital gains taxes.
Like-kind property requirement: The replacement property must be of a like-kind to the relinquished property, meaning it must be held for investment purposes or used in a trade or business. Personal residences and certain types of properties are not eligible for 1031 Exchanges.
Qualified intermediary involvement: Investors must use a qualified intermediary (QI) to facilitate the exchange, holding the proceeds from the sale of the relinquished property until the replacement property is acquired. Choosing a reputable and experienced QI is crucial to ensure a successful exchange.
Before engaging in a 1031 Exchange, it’s essential to consider these requirements and evaluate whether this tax-saving strategy aligns with your financial planning and investments performance goals.
Delaware Statutory Trusts (DSTs) are another tax mitigation strategy available to investors, particularly in the real estate sector. A DST is a legal entity that allows multiple investors to hold fractional ownership of a single property or a portfolio of properties. DSTs are commonly used as replacement properties in a 1031 Exchange, providing investors with the opportunity to diversify their real estate holdings and reduce the management burden associated with direct property ownership.
Potential tax benefits: DSTs can be used as replacement properties in a 1031 Exchange, allowing investors to defer capital gains taxes and maintain the tax advantages associated with their original investment. Additionally, DST investors may be eligible for depreciation and interest deductions, further reducing their taxable income.
Diversification: Investing in a DST allows investors to diversify their real estate portfolio by owning a fractional interest in various properties with different characteristics, locations, and investment objectives. This diversification can help mitigate risk and enhance the overall performance of their portfolio.
Simplified management: As a DST investor, you won’t be responsible for the day-to-day management of the property. The trust is managed by a sponsor, who takes care of property operations, maintenance, and decision-making, freeing you from the hands-on responsibilities of direct property ownership.
Accessibility to institutional-grade properties: DSTs provide individual investors with access to institutional-grade properties that might otherwise be out of reach due to high investment minimums or other barriers. By pooling resources with other investors, you can participate in larger, potentially more lucrative real estate investments.
Despite the benefits, there are some potential drawbacks and risks associated with DST investments:
Limited control: As a fractional owner in a DST, you won’t have direct control over the property or the decision-making process. This lack of control may be a concern for some investors who prefer to manage their investments more actively.
Illiquidity: DST investments are generally illiquid, meaning they may be challenging to sell or exit before the end of the trust’s predetermined holding period. This lack of liquidity may not suit investors seeking short-term investments or those who require more flexibility in their investment strategy.
Risks associated with real estate investments: As with any real estate investment, DSTs are subject to market fluctuations, economic conditions, and other risks that could impact the property’s value and returns.
To help you make an informed decision on which tax mitigation strategy is best suited for your financial planning and investments management goals, here’s a comparison table highlighting the key aspects of Opportunity Zones, 1031 Exchanges, and DSTs:
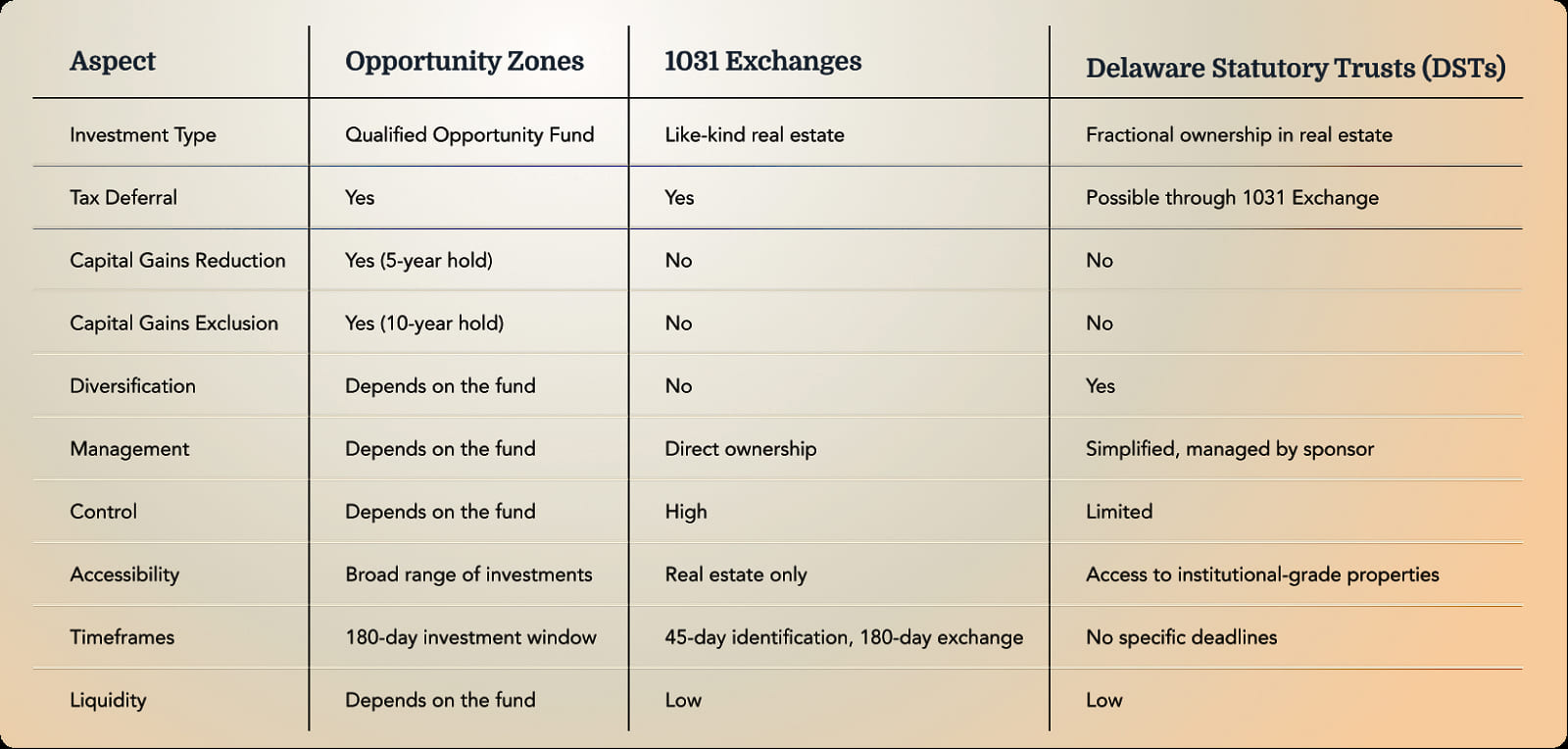
Tax mitigation strategies like Opportunity Zones, 1031 Exchanges, and DSTs can help investors maximize their tax savings and optimize their portfolio in today’s uncertain financial markets. By understanding the unique benefits and potential drawbacks of each strategy, you can make informed decisions that align with your financial goals.
Managing multiple investments, including real estate projects and alternative assets, can be overwhelming. However, with Vyzer, you can streamline your financial planning and investments management. Our secure platform offers clarity, visibility, and automation, all in one convenient dashboard.
Take control of your financial future and make the most of your investments for free. Don’t miss this opportunity to simplify and optimize your wealth management – start your free trial now!